
The treatment of patients with oligometastatic tumor disease in a closed-loop process was the focus of research activities in M²OLIE during the second funding phase. In the first funding phase, a wide variety of steps were successfully researched, including electronic patient education, novel imaging analyses, automated robot-assisted needle placement for biopsy and intervention, molecular classification of tumor entities using mass spectrometry, and convening an ad-hoc tumor board for therapy decision.
The goal of the research activities in the second funding phase was to integrate the previous individual steps into a seamless, time- and cost efficient process, which, by the end of the second funding phase, culminated in a clinical evaluation in tumor patients with individualized, minimally invasive therapy of all metastases.
The research was based on the close interconnection of the three joint projects: M²IBID with diagnostic and interventional imaging and molecular analysis, M²INT with automation and robotic assistance in biopsy and intervention, and M²DATA with the design of an M²OLIE-wide data supply process.
The complete M²OLIE closed-loop process will lead to a paradigm shift in the entire diagnostic and therapeutic treatment process for oncology patients.
The clear identification and characterization of therapy-relevant focal findings using innovative diagnostic methods forms the basis for minimally invasive therapy (including radionuclide therapy) for patients with oligometastases in the closed-loop process of M²OLIE. It also allows prediction of the expected response to therapy and early identification of patients who do not respond to a particular therapy (non-responders).
The aim of the M²IBID joint project was to investigate these basic requirements for determining effective therapy in the sense of “precision medicine.” The techniques of diagnostic and interventional imaging and molecular mass spectrometry (MS) bioanalytics were to be more deeply integrated and clinically evaluated. The innovative research goal was to ideally combine all this information to explore novel tumor characterizations using radiomics approaches and machine learning techniques that improve patient-specific intervention. The M²IBID joint project was carried out on an interdisciplinary basis within the framework of the four subprojects “M²IP,” “M²OT²AN,” “SIM²BA,” and “M²KoRaMo.”
Integration of imaging, molecular bioanalytics, and AI-supported procedures for personalized, and minimally invasive therapy.

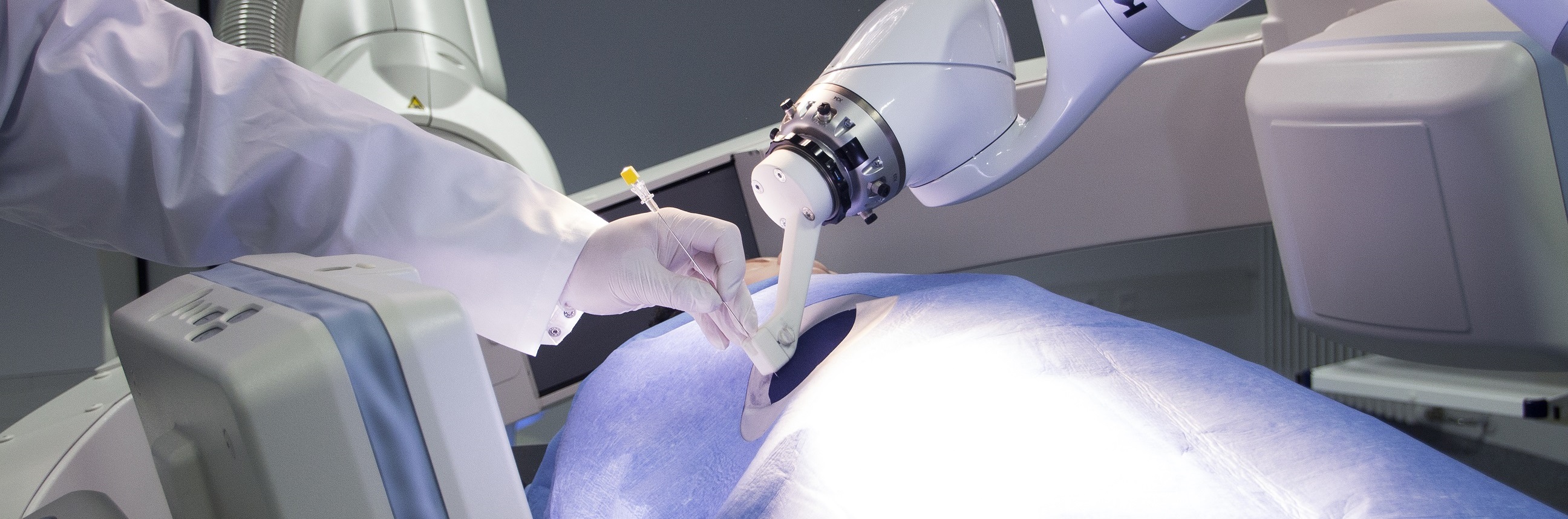
Within the entire M2OLIE closed-loop process, the M²INT joint project focused on the design and optimization of diagnostic and therapeutic processes in the intervention room. Effective treatment requires a condensed, flexible, and efficient sequence of diagnostic and therapeutic measures. In the second funding phase, the aim was to overcome existing limitations and focus on market-ready technologies for the design of future intervention rooms. The overall goal of M²INT as a consortium is the integrated (further) development of medical methods, technical solutions, and processes for the treatment of patients with oligometastases using molecular medicine methods based on the closed-loop principle. At the end of the project, the partial solutions of M²INT in the intervention space are to be integrated into a system and evaluated as part of the entire M²OLIE process in the clinic with patients. Specifically, M²INT aims to increase the efficiency of the interventional process and improve patient outcomes as well as the intraoperative situation in the treatment of patients with oligometastases. Technological developments form the basis for the further development of therapeutic applications, which in turn are to be used as test case for the clinical evaluation of the technologies. In order to achieve these goals, the M²INT joint project consists of three sub-projects in which the necessary partial solutions are being developed: “System platform for molecular intervention applications” (sub-project 1), “Navigated molecular diagnostics and therapy” (subproject 2) and “Methods of molecular intervention” (subproject 3). In addition to the partial results, the overarching innovation lies in the high degree of integration of the overall system, including clinical evaluation. The projects are based in part on the results of the first funding phase of M²INT or adopt them in their entirety.
Optimization of diagnostic and therapeutic processes in the intervention room to increase efficiency, flexibility, and patient outcomes in the M²OLIE closed loop.

The aim of M²DATA was to develop a data lake that would serve as the central data infrastructure for the M²OLIE closed loop. Complex, application-specific data (e.g., data from biopsy needles or robot movements) are converted into a standardized data format, linked to patient information from clinical information systems, and then made available to researchers and physicians in the intervention room. M²DATA helps to provide patients with important medical information about the planned molecular intervention before treatment, to plan the clinical treatment process efficiently and economically, to provide physicians with information relevant to the current procedure, and to enable new medical procedures and findings through a holistic patient picture and the automated analysis of data from previous interventions.
In addition, the data lake creates the conditions for innovative machine learning methods to optimize clinical processes (such as the tumor board process) and data analytics to improve medical treatment. In the medium term, M²DATA will serve as the basis for the further development of the M²OLIE research campus into a platform ecosystem. In order to achieve the goals of M²DATA more efficiently, the project has been divided into three sub-projects: “M²HUB,” “M²OTUS,” and “ProM²etheus.”
Central data lake and applications that standardize and link clinical and technical data, make it available to physicians and researchers, and enable more efficient treatment planning.